PESTLE In Project Management: What Do You Need To Know?
Let’s talk about PESTLE Analysis and how you can use it to make a successful business change. Organisations are always looking to improve and grow, and the way they achieve is via new projects. The right tools like PESTLE help organisations’ and projects’ teams steer the initiative in the right direction for success.
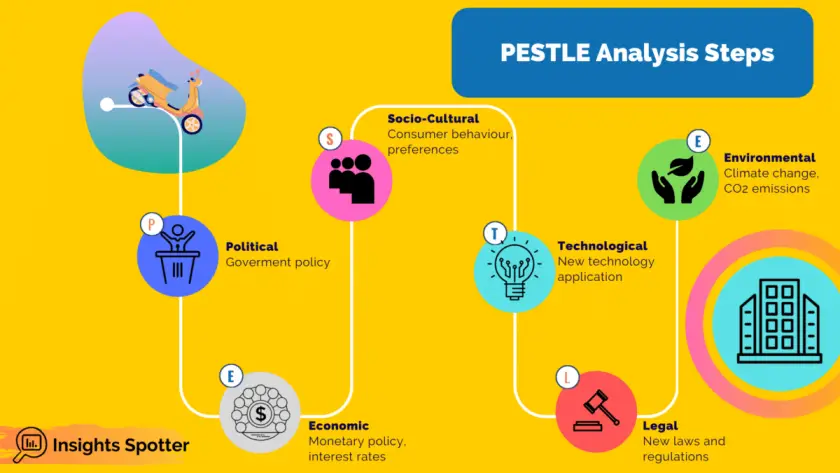
PESTLE is a strategic planning tool used by project managers to systematically evaluate Political, Economic, Socio-Cultural, Technological, Legal and Environmental factors. These factors provide a view of the project’s external operating environment and indicate potential opportunities and threats.
Let’s go through each factor in PESTLE analysis and explain what it means and represents. We will supplement the technical explanation with helpful real-life examples. Finally, we will look into the fictional recreational bicycle manufacture “Two Wheels” as a business case and explore what PESTLE analysis could look like for that business.
Where Does PESTLE Analysis Fit In Project Management?

As a project professional, sometimes you get lucky, and you get to work on starting a new project. I love the initiation phase of the project lifecycle because you get a lot of opportunities to contribute. Everything is new and exciting at this stage, and you will need to help the business with a lot of decision-making. Thus, you should be ready with the right tools to be able to help. Today, we will talk about using the PESTLE analysis for Project Management in an organisation.
When you start a new project, you are looking to positively change the organisation by saving time and money or decreasing operational risks. To achieve such objectives, you need to understand how the project and organisation fit in an existing business environment.
PESTLE gives the project team and business managers an exact list of external factors to consider, which exposes opportunities and threats. Then you combine your PESTLE results with SWAT analysis to get a more rounded picture of the current company environment from an internal and external perspective.
The project management team with business’s representatives should go through each factor and record influences that the company is facing. Then, work on the most optimal way forward to address existing opportunities and threats.
The analysis could provide ideas for an outline of a new project, a seed for the fully-fledged initiative. Thus, you could directly contribute both to steering business’s decisions toward the most profitable outcome and coming up with new promising business initiatives.
There are additional strategic tools you should be using to complete the full SWAT analysis. If you would like to learn more about SWAT analysis and other strategic decision-making techniques, check out my post: HOW TO DO A SWOT ANALYSIS FOR PROJECT MANAGEMENT (+EXAMPLE)
Now, let’s dive into each area of the PESTLE analysis.

Political in PESTLE Analysis
Country Level of Political Factors
At the country’s level, the government influences its environment by issuing new laws and regulations.
Closely linked with new rules and opinions is the government’s stability, where unstable governments create a more challenging business environment. Every time society elects new representatives, we see change. The new government will want to prove that the trust put to them is not baseless and will issue new laws and regulations. For example, historically, Italy and these days, the UK has less stable governments; thus, the rate of new rules increases, increasing instability and cost for businesses.
If your industry can be affected by new elections, you may want to address these threats by implementing more flexible project frameworks like Agile.
International Level of Political Factors
At the international level, you have governing bodies, like the World Trade Organisation, dealing with the trade’s global rules or other international governments. Consideration is relevant for those companies that have international offices or export/trade in different countries.
The prime example recently was how different governments have been dealing with COVID-19, and various measures have been implemented. Companies had to adapt to continue trading.
Other examples could be tax laws and having to pay different tax rates depending on where you operate. Even though this is closely related to the Legal part of PESTLE, our next example is more a political act. Google paid French authorities almost €1bn to settle the tax dispute. They have been trading for years before the fine, but the government needed to show they are in control.

Economic in PESTLE Analysis
The economy is a broad subject, and there are a lot of complex structures. However, at a high-level, there are particular elements, which have a direct impact—for example, interest rates, monetary policy and resulting inflation, consumer saving’s rate and competition.
If your business is in a more favourable economic environment to get more loans or subsidies to start a project, maybe this is where it should get funding for a new initiative. Additional funding could be an excellent opportunity for businesses to increase productivity through new initiatives.
As I write this blog post, the United States has lowered its interest rates by one percentage point, from 1% to an annual rate of 0% based on countryeconomy.com. Of course, banks will have their margin added on top, but lending rates have never been so low.

Socio-Cultural in PESTLE Analysis
Socio-Cultural is all about the business target market. Consumer behaviour, preferences and attitudes are shifting all the time influenced by other factors in PESTLE.
I am sure you could come up with countless examples.
- Like people tend to prefer goods produced in their own country.
- Push for equal pay between women and men at various levels of the organisation.
- Preference to use lower carbon emission products.
- Plan-Based diets are gaining ground. Some industry analysts are saying plant-based meat substitutes might just grab 50% of the meat industry by 2050. according to Forbes
Thus, projects created in these business environments should consider the social angle on the final deliverables.
What Is the Socio-Cultural Impact Of COVID-19?
After COVID-19 hit economies and people started to work from home, there was a visible Socio-Cultural shift when people start buying more items online. Therefore, companies had to adapt and create various projects to move brick and mortar shops online.
If you are a project manager in an organisation with no online presence, it may be evident to you that a new e-commerce website should be established. Yet, do not neglect other PESTLE factors as more than one element could be in play. Thus, complete full analysis to see the whole picture.

Technological in PESTLE Analysis
Technology is a fascinating subject to me and should be to organisations. There is so much happening, from AI to manufacturing or from electric travel to internet services.
For instance, many individuals start working from home due to COVID-19, and companies like Zoom are booming. In April 2020, 46.6% of people in UK employment did some work at home according to ons.gov.uk.
Usually, the advice would be to keep up with the trend and be flexible, or your organisation will be left behind. However, after reading “Great by Choice: Uncertainty, Chaos and Luck – Why Some Thrive Despite Them All” by Jim Collins, I firmly believe it is about making a change in your organisation’s culture and processes first. The technology comes in second as a facilitator but not the catalyst.
It does not mean that you shouldn’t encourage technological change; it means that the project should cover operational cultural and technology changes. Technology is where people will get super excited, thinking that it will solve all their problems, and you could use this to your advantage to increase momentum and buy-in. Still, I would caution stakeholders and make sure any given project has an overarching strategy.
Technology is a tool, and you need the right people and attitudes to use it.

Legal in PESTLE Analysis
Legal would include current and impending legislation that affects your industry in employment, competition, consumer protection, health and safety.
The financial industry was hammered with regulations and new laws aiming to protect consumers after the 2008 financial crises. Banks across the world have paid about $321 billion in fines since the 2007-2008 financial crisis as regulators stepped up scrutiny, according to a note by the Boston Consulting Group as seen in this Reuters article.
Even after considering regulations, you have the country’s courts different attitudes toward large or small companies. As in the Google example before, there was very high interest to slap a nice fine to make an example from a political perspective, but courts would have had to agree with the government.

Environmental in PESTLE Analysis
Finally, we have environment issues like recycling, packaging, carbon emissions, oil consumption and green energy.
One example is different “Green” deals countries attempting to put into legislation. In the US, you have a “Green New Deal”, and in the EU, you already have fixed commitments by 2020. The EU Member States, such that the EU will reach a 20% share of energy from renewable sources by 2020, according to Wikipedia.
Thus, if your organisation is in an industry that deals with carbon emissions like car manufacturing, you may need to brush up on “Green” initiatives before executing a project to ensure a new solution is compliant and future proved.
How to Use the PESTLE Analysis In Project Management?
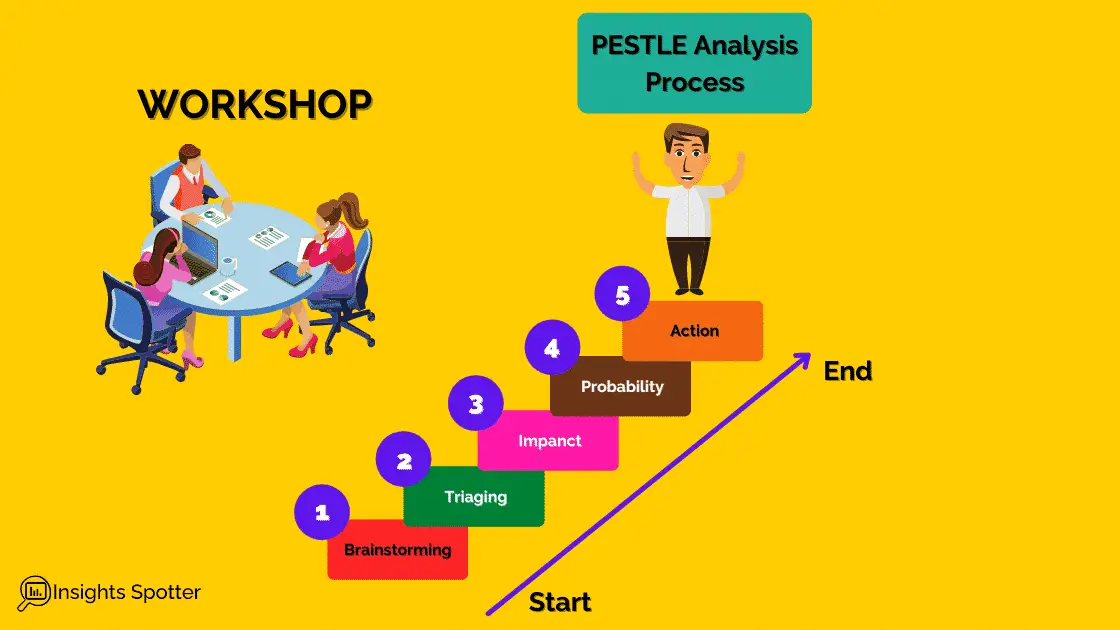
PESTLE analysis is following a similar process to most qualitative risk analysis. You would generate ideas, then validate them and address the ones that are most likely to happen. So you could follow the steps below in your project initiation or planning workshops.
Brainstorming: In project initiation or planning workshops, you would like to go wide first and generate as many as possible factors, which will fall either in threats or opportunities. You could collate ideas through whiteboards, flip-chats, sticky-notes or just open discussion. An informal setting with coffee and some snacks could help with creativity.
Triaging: You have gone wide and have numerous ideas. Some will be great, and some will not be worth it. At this stage, we would do some triaging and filter to the relevant ideas for the project. You could introduce participants voting, common sense or alignment with corporate objectives.
Impact: You have your shortlist of factors that could negatively or positively impact your project. Time to rate the impact for each factor
Probability: After the impact, we need to consider how likely each factor will affect our project. The simplest way to evaluate both impact and likelihood is to allocate a number value from 1-5. 5 is expected to happen.
Actions: Finally, you know your impact and probability. Combining the two will give you a rate of impact on the project if it is anywhere from 15-25. It would help if you actively took action to mitigate the risk or explore the opportunity. Anything lower still worth considering and addressing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a PESTLE Analysis
The advantages of using the PESTLE analysis
- PESTLE is simple and clear to use.
- The point of the tool is to understand the business and, in turn, the project environment.
- The tool gives means to make strategic analysis and decisions systematically.
- The tool identifies opportunities and threats for business and projects, which allows a project team to address them.
The disadvantages of using the PESTLE tool are
- The business and project environment is very complex, and even after completing a full PESTLE analysis, you may not know everything. Thus, the project team may have falls believes about the state of play and can make the wrong decisions.
- Environments are constantly changing, and the tool needs to be updated regularly, which can be challenging. However, it could be part of regular risks & issues review.
- PESTLE might give the best result only when individuals are participating in workshops having different perspectives.
- If additional data sources are required to complete the analysis, it can take time and effort.
- You never know when you are completely finished with the analysis.

Why Is ESG Important In Project Management?
Although PESTLE does not have an explicit section called ESG, I think it is worth considering.
ESG stands for Environmental, Social and Corporate Governance. The point of ESG is to have industry standards for measuring the sustainability and societal impact of an investment in a company or business. The three factors closely linked to PESTLE.
Investment Works Like Confidence Voting
In a publicly-traded company, managers will care about the organisation’s stock demand and price-performance because compensation is usually closely linked with stock prices. Investors are voting by buying company stocks. More confidence that the company performs well, more demand for equity and better prices.
These days, the Socio-Cultural shift to sustainability at all levels of society incentivises business and investors to pay more attention to ESG, which gives a standard measure. If the company can demonstrate a better ESG score, it will likely attract additional interest.
Therefore, if you are working in a publicly-traded company, you would want to consider ESG as part of your PESTLE analysis. Allowing you to make sure that projects can contribute to better stock performance makes senior managers happy, enhances investors’ trust in the company, and gives you a win, win, win scenario.

PESTLE Business Case Example In Project Management
In a few of my other blog post, I have used the Two Wheels case study example. Two Wheels is a fictional company, which is considering to create a new e-bike. Let’s look at how the Two Wheels’ project team may approach PESTLE for their latest project by considering each factor.
Political
- There would be worries that the younger generation could achieve higher speeds without having the right experience and injure themselves or other individuals.
- Considering existing regulations to wear a helmet. Injuries, which happen to kids, typically end up in the news, and politicians become very aware and concern.
- COVID-19 showed that some governments might be encouraging non-public transport forms to avoid spreading the virus, which could come as an opportunity for Two Wheels.
- Promotion of cleaner air in cities could be a driving factor as well.
Economic
- Cost of electricity as compared with oil prices
- Growth of wealth in developing economies and the ability to afford more expensive e-bikes
- Some countries like the UK has high public transport costs
- Decreasing the cost of batteries
- Increasing material cost
- Overcrowded large cities that limit the movement of people
Socio-Cultural
- Interest to be independent, which an e-bike can provide
- Negative opinion about public transport and environment it represents
- Interest to feel ownership of the transport
- Fear of getting infected by COVID-19 in public transport
Technological
- Increase the capacity of batteries
- The decrease in battery charging time
- Increases in mileage/kilometres capabilities
- Lighter materials available to use
- 3D printing and robotics capabilities used in manufacturing speeding up production and increasing the quality
Legal
- Increased safety rules
- Increase in areas available to drive an e-bikes
- The potentially legal implication of injuring somebody on the road while driving an e-bike
- The requirement to safely dispose of batteries
Environmental
- Climate change and CO2 emission concerns
- Air pollution in large cities
- The pressure to use renewable energy
- Promotion to use cycling and e-bikes
- Battery and frame recyclability of the material
PESTLE Analysis: Full List Of Considerations
Below you will find the full list of considerations you can use when completing your PESTLE analysis for project management.
| PESTLE Factors | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Political | Corruption Environmental laws Fiscal policy Foreign trade policy Funding grants and initiatives Government influence Government policy Government subsidies Labour laws Lobbying Political activism Political aims Political leaning Political stability or instability overseas Political system Preferred industries Regulation and deregulation Stability of governments Tax policy Terrorism and military considerations Trade restrictions |
| Economic | Access to debt Consumer confidence Cryptocurrency impact Currency strength Disposable income of businesses Disposable income of consumers Economic growth Exchange rates Financing capabilities Growth rates Inflation rates Interest rates Stock exchange and markets Taxation Unemployment levels Wages rates |
| Social | Attitude to health Attitude to risk Career attitudes Cultural trends Cultural values Customer buying trends Demographics Distribution of wealth Education levels Ethical attitudes Health consciousness Immigration and emigration Industrial reviews and consumer confidence Life expectancy Marriages and divorces Organisational image Population growth Population size Religion Social classes |
| Technological | Access to connectivity Adoption of technology Artificial intelligence (AI) Level of automation Communicating with target markets Communication advances Data analysis Distributing goods and services Emerging technologies (blockchain, AR & VR, etc.) Increased training to use innovation Internet infrastructure Internet of things (IoT) Maturity of technologies Potential copyright infringements The potential return on investment (ROI) Producing goods and services R&D focus |
| Legal | Advertising standards Competitive legislation Consumer protection laws Copyright and patent laws Discrimination laws Education laws Employment laws Equal opportunities Future Legislation Health and safety laws Privacy laws Product labelling Product safety Safety standards |
| Environmental | Attitude to green technology Carbon footprint Climate and weather Climate change Environmental legislation The geographical location (and accessibility) Pollution and greenhouse gas emissions Promoting positive business ethics and sustainability The decline of raw materials |
PESTLE Analysis Conclusion
PESTLE is a powerful tool that gives an excellent overview of external factors, opportunities and threats. It allows you to consider the current business environment from various perspectives. Plus, you can combine the tool with SWAT analysis to get a more holistic picture of the business or the project.
Let us know in the comments below if you will be using PESTLE in your next project or business consideration.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Latest Blog Posts
- Navigating Project Management in a Matrix Organization: Challenges and Solutions
- Using Artificial Intelligence’s Power in Agile Project Management
- Sustainable Project Management: Trends, Tools, & Strategies
- Unlocking Strategic Value: How NIST CSF 2.0 Shapes Project Choices for Better Outcomes
- Cybersecurity Project Management: Protecting Your Digital Frontier
- What are the Different Types of Planning in Project Management?